Axons
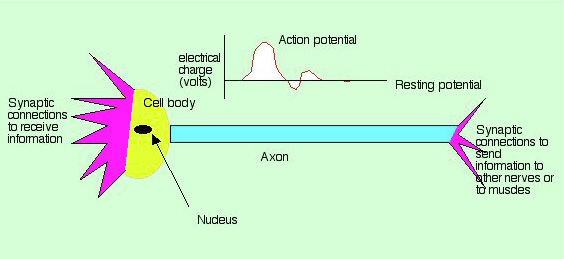
The axon is the basic cell of the nervous system. Axons come in many sizes and shapes, but they all have the same essential structure, which is diagrammed below. When the cell is at rest, there is an electrical difference between the inside of the cell and the surrounding fluid; this is called the resting potential. The nervous impulse, or action potential, starts when the cell membrane is stimulated by a neurotransmitter or by a sensory input. This stimulation causes the cell membrane to depolarize (change electrical charge). We can visualize the depolarization as a wave on an oscilloscope, as shown in the diagram. The action potential passes the length of the axon and then is transmitted to another nerve, or to a muscle. The connections with other nerves or with muscles are called synapses.
page 2-*
copyright ©2002 Michael D. Breed, all rights reserved